Ever wondered how cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin operate securely without a central authority? The answer lies in distributed ledger technology (DLT). But what exactly is DLT, and how does it differ from blockchain? Let’s dive into the world of decentralized record-keeping and explore the nuances of these innovative technologies.
What is Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
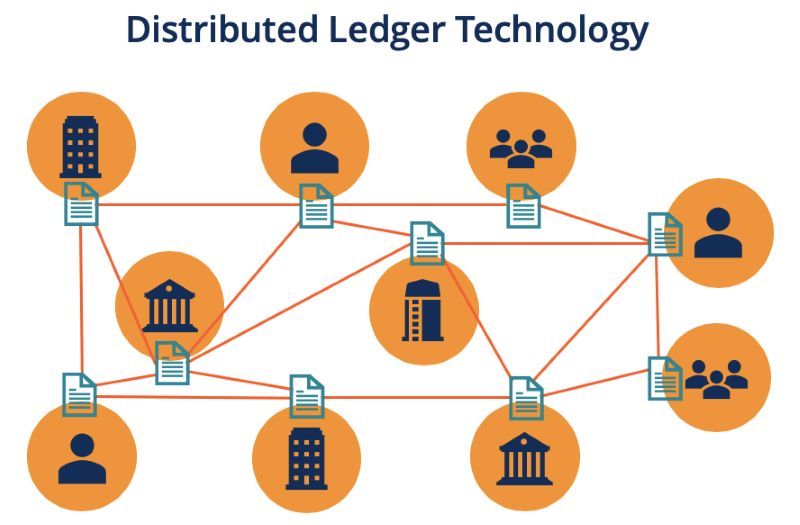
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a digital infrastructure that leverages a network of independent computers to record, share, and synchronize transactions. Its decentralized nature distinguishes it from traditional databases, as it operates without a central authority controlling the data. Instead, transactions are processed by each node in the network, and consensus is achieved through a voting mechanism, ensuring that all nodes maintain identical copies of the ledger. This innovative approach provides a secure and transparent system of record, offering new possibilities beyond those of a simple database.
What does Distributed Ledger Technology use for?
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) offers transformative potential across multiple sectors. In finance, it presents a faster, cheaper, and more accessible solution for transactions, especially in regions with limited banking infrastructure. The immutability, encryption, and security of DLT make it ideal for digital identity verification, curbing identity theft and data breaches. Moreover, DLT’s transparency and immutability can be leveraged to create secure and fraud-resistant voting systems, enhancing the integrity of the voting process.
In addition, DLT can be applied to record property transactions, providing an immutable source of information about ownership and transfer of assets, though transferring ownership of physical assets to the ledger presents some challenges. Overall, DLT’s versatility and unique features offer a range of potential applications beyond its well-known use in cryptocurrencies.
How does the Distributed Ledger Technology work?
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) operates through a network of independent nodes, each individually maintaining and updating the database. When a transaction occurs, its details are disseminated to all nodes for independent analysis and processing. Consensus is reached through a voting mechanism where a majority (often 51%) of the nodes must agree to accept the transaction. Upon reaching consensus, all nodes update their copies of the database to ensure consistency, and the new transaction is recorded in a block on the DLT.
The data stored on the DLT is encrypted using cryptography, ensuring access is restricted to authorized participants. This encryption is also why digital currencies within the blockchain are termed “cryptocurrencies.”
DLT is designed so that modifying even a single piece of information alters the entire database, making it immutable. This immutability, combined with a rules-based governance structure among nodes, creates a transparent and democratic environment. Additionally, the distributed, private, and encrypted nature of DLT makes it resistant to hacking attempts. Since backups are securely maintained across the network, a successful attack would require compromising the entire network simultaneously, a task considered highly improbable.
What are different between DLT and Blockchain?
| Feature | Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) | Blockchain |
| Definition | A broad term for any decentralized database system that records and shares data across multiple nodes. | A specific type of DLT that uses a chain of blocks to record and verify transactions. |
| Structure | Can have various structures, including blockchain, directed acyclic graph (DAG), hashgraph, etc. | Uses a linear, chronological chain of blocks linked together using cryptography. |
| Consensus Mechanism | Can use various consensus mechanisms, including PoW, PoS, PoA, DPoS, etc. | Typically uses PoW or PoS, although other mechanisms are being explored. |
| Use Cases | Wider range of applications, including both public and private use cases. | Primarily used for cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications (dApps). |
| Transparency | Can be public or private, depending on the specific implementation. | Typically public, with all transactions visible to all participants. |
| Immutability | Can be immutable or mutable, depending on the specific implementation. | Immutable, meaning that data cannot be altered or deleted once recorded. |
| Examples | Corda, Hyperledger Fabric, IOTA, Hedera Hashgraph | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin |
| Strengths | Flexibility, adaptability to various use cases, potential for higher scalability. | Security, transparency, decentralization. |
| Limitations | Can be less secure and transparent than blockchain, depending on the specific implementation. | Can be slower and less scalable than other DLTs, especially those using PoW. |
The Future of Distributed Ledger Technology
The emergence of distributed ledgers marks a revolutionary shift in how information is collected and exchanged, impacting both static and dynamic data. This technology transcends traditional databases, focusing on how we utilize, manipulate, and derive value from data.
Currently, distributed ledger technology (DLT) is reshaping the digital landscape by enabling secure data storage, transfer, and management across decentralized networks. Notably, DLT is poised to revolutionize capital markets, impacting everything from securities issuance to settlement, trading, and servicing, with benefits such as faster processing, increased transparency, reduced costs, and mitigated risks.

Beyond the financial sector, this era is witnessing the growing adoption of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, heralding a digital technology-driven society. With the potential of DLT extending beyond cryptocurrencies, its future appears bright as developers continue to innovate and enhance its capabilities. The ongoing exploration and advancements in DLT promise a future where it plays an even more integral role in shaping various industries and aspects of our lives.
While DLT and blockchain are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct concepts. DLT encompasses a broader range of decentralized ledger systems, while blockchain is a specific implementation of DLT. Understanding their differences is crucial for grasping the evolving landscape of decentralized technology and its potential applications in various industries, including finance.
Interested in the latest developments in blockchain and its impact on financial markets? Stay informed with Forex Trend News, your source for in-depth analysis and insights into the evolving world of decentralized finance.

