What is DAG Blockchain? This groundbreaking technology solves the limitations of traditional Blockchain, particularly regarding transaction speed and cost. This article will help you gain a better understanding of how DAG Blockchain works, its notable advantages, and real-world applications across various industries.
What is DAG Blockchain?
DAG Blockchain is an alternative data structure to traditional blockchain, where transactions are not grouped into blocks like in blockchain. Instead, each transaction is linked to other transactions through a directed acyclic graph (DAG). This technology provides significant improvements in transaction processing, network scalability, and transaction cost reduction.
In DAG Blockchain, each transaction acts as a node in the graph and is validated by other transactions instead of waiting for a new block to be created and mined, as in traditional blockchain. This structure allows transactions to be processed concurrently, solving congestion issues and increasing transaction speed.

A key feature of DAG is that it does not require a mining network like traditional blockchain. This reduces costs and transaction processing time, while offering a more decentralized network model. DAG Blockchain promises to be a breakthrough technology for applications requiring high scalability and fast transaction speeds, such as payment systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), and decentralized finance platforms.
So, what is the main difference between DAG Blockchain and traditional blockchain? Traditional blockchain uses a chain of blocks linked together, whereas DAG does not have blocks but a graph where transactions are confirmed through connections with other transactions. This helps reduce network congestion and allows handling large volumes of transactions simultaneously, without the issues faced by traditional blockchain.
How DAG Blockchain works?
The operational mechanism of DAG Blockchain is distinctly different from that of traditional blockchain systems. While traditional blockchain requires transactions to be recorded into blocks and validated through mining, DAG Blockchain uses a completely different data structure for transaction processing. Here’s how DAG operates:
- Transaction processing: Each transaction in DAG is not grouped into a block but becomes a vertex in the graph. To validate this transaction, it must be confirmed by prior transactions. This validation process occurs concurrently with other transactions in the network, without waiting for a new block to be created. This reduces waiting times and speeds up transaction processing.
- Decentralized structure: In DAG, the network does not require a central node to control and validate transactions. Instead, transactions are validated through the cooperation of distributed nodes in the network. This not only enhances decentralization but also minimizes the risk of potential attack points.
- Consensus mechanism: DAG uses a cooperative consensus mechanism rather than systems like Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS) in traditional blockchain. Nodes in DAG collaborate to validate transactions instead of competing with each other. This not only saves energy but also increases transaction processing speed and efficiency.
- Scalability: One of the biggest advantages of DAG is its scalability. Since transactions are processed concurrently and do not require waiting for new blocks, DAG can handle thousands of transactions per second without experiencing congestion. This is a crucial factor that makes DAG an optimal solution for applications requiring high speed and scalability.
- Cost efficiency: Without the need for mining processes, DAG minimizes transaction costs and does not require high transaction fees like traditional blockchain networks. This is especially useful in IoT applications or small-scale transactions, where low cost and speed are critical.
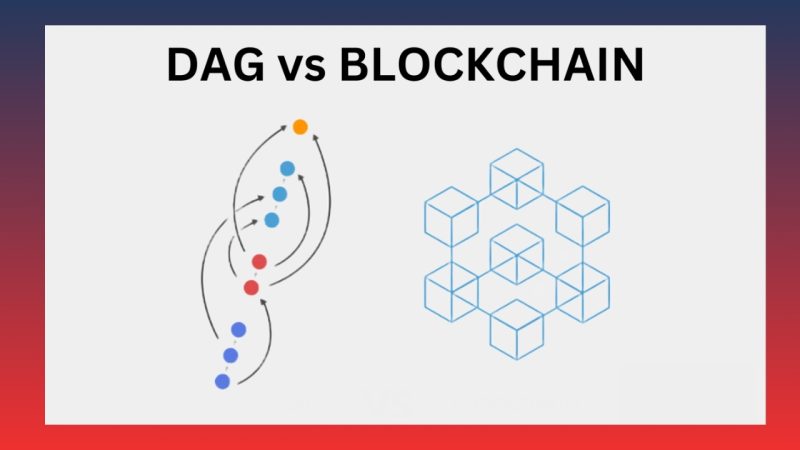
Comparison between DAG Blockchain and traditional Blockchain
When comparing DAG Blockchain and traditional blockchain, we can clearly see the differences in structure, transaction processing mechanisms, and scalability of each type.
- Transaction processing speed: In traditional blockchain, each transaction is grouped into a block and must be mined before being added to the blockchain. This process causes delays and limits the number of transactions the network can process within a given time. In contrast, DAG Blockchain allows transactions to be processed concurrently, thanks to its graph structure, without waiting for mining processes, significantly reducing transaction time.
- Transaction costs: Traditional blockchain transactions typically incur transaction fees because miners must solve complex problems to mine and validate transactions. In contrast, DAG Blockchain does not require mining, significantly reducing transaction costs, or in some cases, transactions can be processed for free.
- Scalability: Traditional blockchain networks are limited in scalability, especially as the number of transactions increases. Popular blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum have relatively low transaction speeds and often experience congestion. DAG Blockchain, with its ability to process transactions concurrently without waiting for new blocks, can scale efficiently without facing the same issues.
- Security: Both traditional blockchain and DAG have strong security mechanisms, but their approaches to security differ. In blockchain, transactions are secured by mining nodes and the consensus mechanism of the network. In DAG, security is ensured by validating transactions through links between transactions, reducing the risk of a 51% attack that traditional blockchain may face.
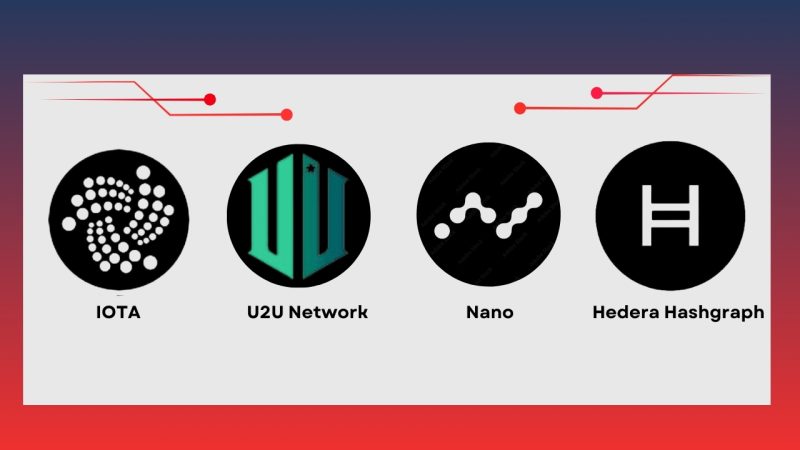
Practical applications of DAG Blockchain
DAG Blockchain is not just a theoretical technology; it has been applied practically in various industries, particularly in sectors that require high scalability and fast transaction speeds.
- IOTA and IoT: IOTA is a cryptocurrency project using DAG to solve transaction issues in IoT networks. Each device in the IoT system can transact directly with other devices without the need for an intermediary. DAG enables IOTA to process these transactions without fees, making it an ideal platform for IoT, where low-cost transactions are essential.
- Nano: Nano is a cryptocurrency that uses a “block-lattice” structure, a form of DAG, to ensure that each account has a unique chain for processing transactions. This reduces latency and eliminates transaction fees, making it an ideal solution for quick, decentralized payments.
- Hedera Hashgraph: Hedera Hashgraph is a blockchain platform based on DAG that uses the “gossip about gossip” consensus mechanism, enabling thousands of transactions per second. This makes Hedera Hashgraph a perfect choice for financial applications, smart contracts, and applications requiring the processing of large data sets.
- U2U Chain: U2U Chain, a decentralized blockchain, also employs DAG technology to enhance scalability and security for decentralized finance and IoT applications.
Thus, this article has provided a detailed explanation of “What is DAG Blockchain?” DAG Blockchain is a technology that promises to transform the way distributed networks operate. With its fast transaction processing, low costs, and high scalability, DAG is becoming the ideal platform for financial, IoT, and big data applications. While there are still challenges to overcome, DAG Blockchain’s exceptional potential ensures that it will play a significant role in the future of blockchain technology and decentralized applications.
For the latest insights and updates on technology and investment markets, don’t forget to follow the newest articles on Forex Trend News.


